binfalse
Challenge is over.
November 28th, 2013About 6 or 10 moths ago we were searching for a student to work with us in the SEMS project. In order to reduce the number of applications I started a challenge. To solve this challenge you had to show some understanding for basic techniques and programming languages, so we didn’t waste our time with people not able to write a single line of source code.
And what should I say? It was successful! We’re now a great team with three students :D
However, currently this challenge seems to spread over the internet. And lot’s of people try to solve it (and many submit a wrong answer^^). But even worse, some of you guys try to exploit it by submitting something like
"; SHOW TABLES;In general I don’t care. It was just some lines of PHP that send me an email in case of a correct answer. There is no database and the worst that can happen is a full inbox, but now I decided to close this challenge and instead forward users to this article.
Thus, if you arrive here feel free to apply for a job! I guess all of my readers, even if they didn’t solve this challenge, are perfect fellows…
If you nevertheless want to give it a try you can download the challenge.
Extended MyTinyTodo
November 5th, 2013MyTinyTodo is a self-hosted todo-list which convinces by its simplicity. It allows to maintain several different lists, you can assign tags, priorities and due dates to certain tasks. I used it myself for a long time and decided to fork the project in order to implement some stuff I missed in the original version.
I do not intend to talk about MyTinyTodo a great deal. Very tiny, does nothing that isn’t necessary. No Dropbox/Facebook/Instagram etc integration. I really like this kind of software :D
But I was missing an essential feature: Creating tasks via mail.
Lucky us, MyTinyTodo is distributed under the terms of GPLv3 license. Thus, I hg clone d and extended the tool with desired functionality. And since the IDE was already opened I added a tiny authentication (now: username + password; previously: .htaccess ) and secured the API by introducing a signature. Nothing special or complex, but it had to be done.
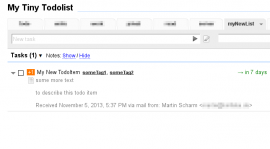
Long story short: I’m now able to submit tasks via e-mail. That means, a mail containing the following:
To: todo@your.server.tld
Subject: My New TodoItem
some more text
to describe this todo item
priority:1
tags:someTag1,someTag2
duedate:nextweek
list:myNewListwill result in something similar to Figure 1. All possible attributes that are recognized in the mail body are listed at the wiki on GitHub.
Find out more on GitHub.
Integrating Tomcat with Apache
October 4th, 2013You can configure the Apache web server to forward requests to Tomcat. Thus, you can speak to both servers on ports 80 or 443 and get rid of the :8080 for your Tomcat applications. I’m somehow doing that very often, so here is small how-to for copy&paste purposes.
Install jk
As you might know, while Tomcat is Java stuff Apache is written in C. So in general it’s not that easy to get them talking to each other. The key to achieve an integration is called mod_jk (see The Apache Tomcat Connector). So first of all you need to install it:
aptitude install libapache2-mod-jkIf it is installed you can configure an AJP worker in /etc/libapache2-mod-jk/workers.properties
:
# Defining a worker named ajp13_worker and of type ajp13
# Note that the name and the type do not have to match.
#
worker.ajp13_worker.port=8009
worker.ajp13_worker.host=localhost
worker.ajp13_worker.type=ajp13As soon as this is done the bridge is ready to close the gap between Apache and Tomcat.
Configure Tomcat
We need to configure an AJP connector on port 8009 . So open /etc/tomcat7/server.xml and add another connector next to the other ones:
<Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" address="127.0.0.1"/>If you’re lucky there is already such a connector defined in the comments. So just remove the comment…
Configure Apache to speak through jk
Here I’ll show you how to setup a virtual host. For example, copy the following to /etc/apache2/sites-available/012-yourapp.conf :
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin some@body.tld
ServerName yourapp.yourserver.tld
ServerAlias ya.yourserver.tld
RewriteEngine on
RewriteRule ^/(.*)$ /YourApp/$1 [L,PT]
JkMount /* ajp13_worker
</VirtualHost>Ok, let me shortly explain what I did there.
- Everything that arrives at this vhost gets forwarded to our previously defined AJP worker (line 9)
- I assume your Tomcat webapp is running on
server:8080/YourApp, therefor I configured a substitution of the URL to insert/YourApp(line 7). Of course you need to havemod_rewriteinstalled and enabled. (You may skip this line if you’re fine with having/YourAppin all your URLs) - The rest should be clear. The vhost is available at
http://yourapp.yourserver.tld, as well as athttp://ya.yourserver.tld(lines 3&4). You can also use SSL, just configure line 1 to listen at*:433and add the SSL stuff to the body of your vhost. (SSL exmaple)
Afterwards, enable the vhost to populate it:
a2ensite 012-yourappGive it a try
If this is done just restart everything:
service tomcat7 restart
service apache2 restartNow Apache forwards all requests to http://yourapp.yourserver.tld to your Tomcat webapp at http://yourserver.tld:8080/YourApp .
Find all Text Files, recursively
June 30th, 2013Because I was thinking of something like that for a long time.
In bash/zsh (add it to your .rc ):
textfiles ()
{
file $(find $*) | /bin/grep -E 'text|empty' | cut -d ':' -f1
}Using this function it’s possible to open all text files of a project at once:
kate $(textfiles project/*)Change Title of moderncv Document
June 21st, 2013Once again I had to prepare a CV for an application. I’m using the moderncv package to create the CV in \(\LaTeX\) and I was always bothered about the title of the document. Today I spend some time to fix that.
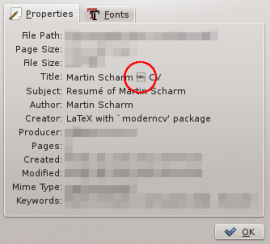
Using moderncv you can produce really fancy CV’s with very little effort. But unfortunately, by default it produces an ugly title (see the screenshot taken from Okular). As you can see, there is some character that cannot be displayed by certain tools.
I guess most of my “CV-reviewers” don’t care about this little issue, if they recognize it at all, but it bothers me whenever I have to create a resumé. I already tried to override it using the hyperref package, but wherever I put the statement it seems to have no effect.
However, since moderncv is open source (yeah! lovit) I took a look at the code to see how they produce the title. It was quite easy to find the concerning statement (in my case /usr/share/texlive/texmf-dist/tex/latex/moderncv/moderncv.cls:96 , texlive-latex-extra@2012.20120611-2):
\AtEndPreamble{
\@ifpackageloaded{CJK}
{\RequirePackage[unicode]{hyperref}}
{\RequirePackage{hyperref}}
\hypersetup{
breaklinks,
baseurl = http://,
pdfborder = 0 0 0,
pdfpagemode = UseNone,% do not show thumbnails or bookmarks on opening
pdfpagelabels = false,% to avoid a warning setting it automatically to false anyway, because hyperref detects \thepage as undefined (why?)
pdfstartpage = 1,
pdfcreator = {\LaTeX{} with `moderncv' package},
% pdfproducer = {\LaTeX{}},% will/should be set automatically to the correct TeX engine used
bookmarksopen = true,
bookmarksdepth= 2,% to show sections and subsections
pdfauthor = {\@firstname{}~\@familyname{}},
pdftitle = {\@firstname{}~\@familyname{} -- \@title{}},
pdfsubject = {Resum\'{e} of \@firstname{}~\@familyname{}},
pdfkeywords = {\@firstname{}~\@familyname{}, curriculum vit\ae{}, resum\'{e}}}
\pagenumbering{arabic}% has to be issued after loading hyperref
}As expected the pdftitle contains a double-hyphen that is converted by latex to a dash. Apparently a problem for some programs. To fix this issue you could sudo:modify this file, but that’s of course messy. Better add something like the following to the end of the header of your document:
\AtEndPreamble{
\hypersetup{pdftitle={Your New Title}}
}This will override the broken output of the package.